Osteoarthritis, or rheumatoid arthritis, is an inflammatory disease of the bones and joints. It occurs when Mycobacterium tuberculosis infects the joints, most commonly the feet, legs, and ankles.
Symptoms include joint pain, swelling, and weakness. Diagnosis involves imaging tests and biopsy. Treatment requires long-term antiretroviral therapy and frequent surgery.
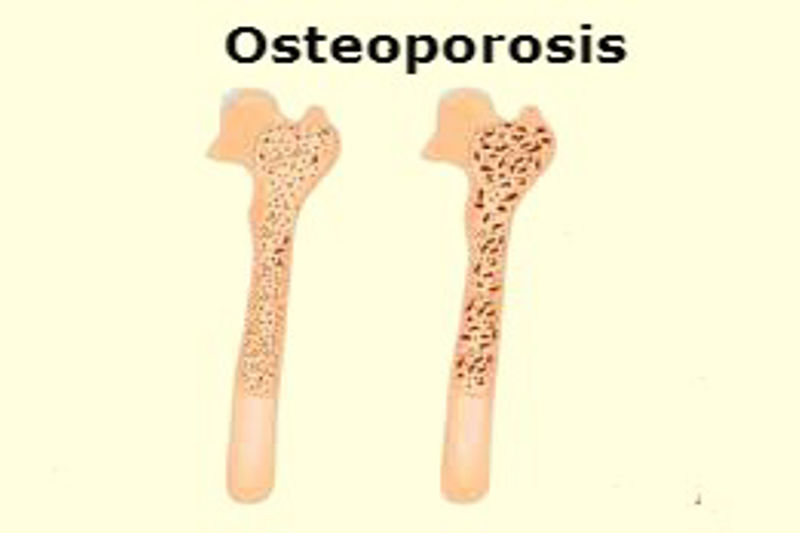
Types of Osteoporosis?
Tuberculosis of the bones, also known as knee or bone tuberculosis, has several subtypes, depending on where it is located in the bone, such as:
• Osteoarthritis (Pott’s disease): An infection of the bone, leading to bone loss and possible fractures.
• Osteoarthritis: Involves the bones outside the bones, such as the long bones and joints, leading to wear and tear.
• Osteoarthritis: An inflammatory disease of the bones, characterized by joint pain, swelling, and arthritis.
• Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints, such as the hips or knees, leading to joint damage and weakness.
• Tendonitis: Inflammation of the skin, causing inflammation and swelling.
What are the symptoms of osteoporosis?
Diagnosing tuberculosis can be challenging, especially since tuberculosis is often asymptomatic and painless. Patients may not show symptoms until the disease is advanced. In addition, tuberculosis can appear in the brain and spread unexpectedly. However, when bone cancer occurs, some basic symptoms appear, such as:
• Severe back pain.
• Stiffness.
• Abscess.
As osteoporosis worsens, a number of symptoms appear, including:
• Neurological problems.
• Paralysis or paralysis.
• Children have more widespread problems.
• Bone problems.
Interestingly, symptoms associated with tuberculosis, such as fatigue, fever, night sweats, and weight loss, are not always seen in osteomyelitis. The disease requires monitoring due to its insidious onset and potentially serious side effects.
What are the causes of breast cancer?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a harmful bacterium that is often transmitted by a pneumococcal pathogen, especially with pneumococcal vaccines.
• Weakened immune system: HIV and diabetes increase the risk of cervical cancer.
• Direct infection: An injury or surgery can spread breast cancer directly to the nerves and tissues.
• Bloodstream infections: Blood cancer can spread to the bones.
• Exposure to people with syphilis, increases the risk of cervical cancer.
The disease is usually transmitted through the mouth. Musculoskeletal damage can occur if antibiotics are not administered promptly. Early detection and management are essential for effective treatment.
What problems cause asthma? Tuberculosis (TB) is a common disease that can worsen if left untreated.
• Arthritis: Inflammation of the joints can cause muscle weakness, tears and weakness.
• Arthritis: Destroys surrounding joints, reduces function and causes physical infection.
• Fatigue: chest and neck pain, headache, and muscle aches.
• Depression: Pneumonia causes severe brain swelling.
• Chronic pain: Chronic pain interferes with mobility and normal life.
Weight loss: If tuberculosis is not treated, it can spread to the bones and other parts of the body.
• Chronic pain: This is a normal part of the body and can cause serious neurological problems.
• Secondary kidney damage: Chronic kidney damage leads to secondary kidney disease. • Common symptoms include fever, weight loss, and other symptoms of kidney disease.
• Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment with anti-TB drugs are essential to prevent complications Severe cases may require surgery to correct deformities and restore function, as well as regular monitoring for full recovery and long-term complications.
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
Tuberculosis (TB) requires a thorough examination, including a biopsy procedure:
The tests
Initial assessment includes physical examination and laboratory tests such as joint pain, muscle weakness, and swelling.
Image tests.
The following activities are helpful:
• X-Rays: Check for fractures, fractures, and fractures.
• CT Scan: Detailed images of bone.
• Magnetic resonance imaging: helps in early detection and exclusion of bony changes.
Laboratory tests.
Competitions such as:
• Blood tests: diseases that are related but not related.
Blood tests: IGRA immunoglobulinemia & C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), C-reactive protein (CRP) response, inflammatory and anti-inflammatory activity.
Microbiological examination.
Bacterial cultures and PCR tests are used for primary diagnosis.
The diagnosis is made when clinical examination and laboratory tests show the presence of rheumatoid arthritis.The symptoms vary, but the combination of these symptoms can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
How is skin cancer treated?
There are many benefits of TB treatment, including:
• Anticoagulants: Medications used to treat osteoporosis include isoniazid, steroids, and corticosteroids.
Ways to prevent osteoporosis are:
• Vaccination: Consider BCG vaccination to prevent severe illness.
• Hygiene: Wash your hands frequently, reduce the risk of infection.
Avoid systemic problems: Avoid close communication with the patient.
Early detection: Seek medical attention immediately if you develop signs or symptoms.
• Treatment of tuberculosis: Recommended for high-risk patients.
Surveillance: To prevent the spread of TB.
Follow your doctor’s instructions: Follow your doctor’s instructions to avoid getting sick.
Incorporating vaccination, hygiene and other TB prevention measures into your lifestyle can reduce your risk.
Conclusions: Although rare, osteoporosis still remains a public health problem due to its negative impact on bone health. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for a person to recover and avoid serious illness. To treat this condition, it is important to recognize the symptoms and seek immediate medical attention. It is important to see a chiropractor. Early detection and treatment can help us diagnose and treat the condition more effectively.